Heptapod
Heptapod Cloud and Runner is a SaaS DevOps platform, managed by Clever Cloud. It is based on the open-source Heptapod, a variation of GitLab Community Edition supporting Git and Mercurial.
Overview
The Heptapod DevOps platform is edited by Octobus, a team of experts with experience in Mercurial and Rust, derived from Gitlab Community Edition.
Clever Cloud users can benefit from Heptapod Cloud software, along with Heptapod Runner for CI/CD operations.

Heptapod and Runners
Heptapod Cloud
Heptapod Cloud comes with the following benefits:
- Cost Reduction: No licensing or application maintenance costs, flexible and competitive usage-based pricing per active user.
- Automatic Updates: Heptapod aligns with the continuously evolving GitLab, ensuring you effortlessly benefit from the latest features and security patches.
- Technical and Functional Support: Whether for technical or functional questions, support teams are ready to answer all your queries.
- Scalability: As your team grows or you manage dozens or hundreds of small or large projects for testing and deployment, Heptapod Cloud is designed to handle it. Increase capacities or quantities of CI/CD runners associated with your projects, those of runtimes, storage, or databases managed by Clever Cloud, or adjust bandwidth to handle heavy loads. All these services are native and structured to meet your scaling needs with ease.
Heptapod Cloud provides your team with a suite of collaborative tools for software or document production management:
- Team, Collaborators, and Access Rights: Add and manage team members, organise roles and access rights based on projects.
- Git and Mercurial Repository Management: Heptapod provides a robust and intuitive repository management system for Git and Mercurial, allowing you to effortlessly create, manage, and collaborate on your codebase or documents. With advanced version control and branch management features, you can easily track changes, merge your code, and maintain the integrity and history of your private or public projects.
- Project Management and Ticket Tracking: The ticket tracking system allows you to efficiently manage tasks, incidents, and collaborate seamlessly with your team. Stay organized by setting milestones, qualifying with labels, and customising workflows for advanced control of your operations.
- Collaboration and Code Review: Heptapod provides a wide range of features for effective collaboration, code or document reviews, online comments, and real-time collaboration tools. Work seamlessly with your team, track exchanges, merge requests, and improve the overall quality of your projects.
- Embedded Wiki and Documentation: Knowledge sharing is crucial for high-performing teams. Easily create and maintain comprehensive documentation for your projects, centralise and share knowledge, and provide a smooth experience for new collaborators.
Accessing Heptapod Cloud
Using Heptapod Cloud require a Clever Cloud account and an organization.
Create an organization
You will need a Heptapod group to create your projects in. Heptapod groups are mapped to Clever Cloud organizations. Every organization you have access to will have its corresponding group on the Heptapod Cloud instance.
In the Clever Cloud console, click Add an Organization and fill the form to create one. Organization are the way users collaborate and share applications.
Access to Heptapod via SSO
Accessing to Heptapod Cloud is done with the built-in of Clever Cloud. To launch Heptapod Cloud go to https://heptapod.host.
Usage and billing
Heptapod Cloud is billed on a per-usage model, explained and simulated on our product page.
You can check your Heptapod Cloud usage of repositories and users in the Shared Software tab of your organization.
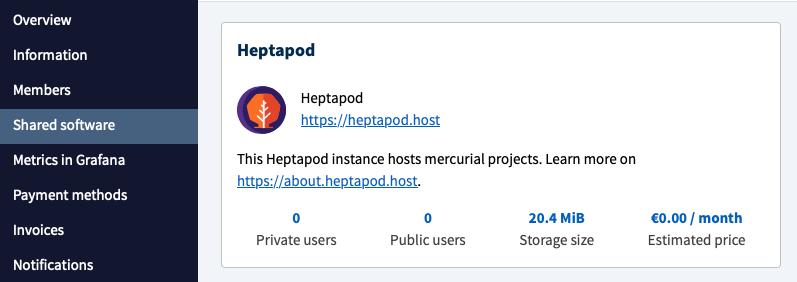
You can check your organization’s Heptapod usage in the Share
Clever Cloud Runners for Heptapod enable on-demand generation of Docker containers of different sizes (Flavors). Therefore Heptapod runners are billed in the same way of runtimes. The pricing is different, and shown on a per-1000 minutes in the Heptapod Runner product page.
Heptapod Runner
Clever Cloud Runners for Heptapod is a SaaS that automates the execution of tasks on machines of varying sizes and power to best match your continuous integration and deployment needs. Fully integrated with Heptapod Cloud, the service can also be used from a self-managed Heptapod or GitLab instance, either managed by Clever Cloud or self-hosted on your infrastructure.
Integrated CI/CD
Clever Cloud Runners for Heptapod comes with the following features:
- Quick activation: Activate Clever Cloud Runners for Heptapod for your organization with just one click.
- Easy customization: Easily define your pipelines using templates for the most popular languages. Edit and validate definitions from the interface or directly from the project file.
- Integrated tracking: Monitor the execution of your tasks in real time, receive notifications of pipeline success or failure, and view activity reports online.
- Components Catalog: Connect your repository to Clever Cloud and deploy on production, create review apps, and automate tasks.
Provisioning
With the Clever Cloud Runner, you may run a great number of parallel jobs, paying for your actual consumption without any threshold effect.
Each time it takes a job, the Clever Cloud Runner spawns a virtual machine within your Clever Cloud Organization.
While the job is running, the virtual machine is visible in the Clever Cloud console, in which each job corresponds to an Application having exactly one instance attached. The instance is the virtual machine running the job.
The type of the instance is “Heptapod Docker Runner”, and is identified by a Heptapod icon. The job number is included of the Application name, which looks like hpd-job-kvzWdEMo-275833.
Both Application and Instance are removed as soon as the job completes, whatever end status was returned to the coordinator. You will be billed for the time the instance was up, with a 10-second granularity.
The pricing will vary on the selected flavour (size, see also below), which is “M” by default. Check it out on the Clever Cloud pricing page, under the “Heptapod Runner” section.
Activation
On heptapod.host, the Shared Runners are disabled by default at Group creation time, and Projects created while they are disabled on the Group also will have them disabled.
This is nothing but the standard GitLab mechanism. If you maintain your own Group or Project runners, this makes sure the Clever Cloud Runner does not steal jobs from them, as chances are high that they would require a specific setup. Also, this avoids billing users for a service that they did not ask for and may not be aware of.
In order to have the Clever Cloud Runner take your jobs, simply activate the shared runners on the wished Groups and Projects:
- Navigate to the Group Settings CI/CD page.
- Expand the Runners section.
- You will be able to activate the shared runners directly from there or allow Projects or sub-Groups to override the Group setting in case you don’t want to activate on the full Group.
- Always check the resulting configuration in the Projects Settings CI/CD pages, and correct it if needed. Changes in the Group Settings are not always immediately taken into account on enclosed Projects.
Running only the Clever Cloud Runner
In case you’d like to make sure that your jobs are taken by the Clever Cloud Runner, only, you can flag them with the clever-cloud job tag.
Here is an example where the tag is set on all the jobs in the CI/CD configuration in one stroke, thanks to the default global keyword:
default:
tags:
- clever-cloud
lint:
script:
- ci/lint
tests:
script:
- ci/run-all-testsWorking like any Docker-based Heptapod or GitLab Runner
Except for provisioning, everything happens as if the job was launched by a standard Docker executor, with only a handful of differences (see the dedicated subsection).
To simplify, you can create a Docker image containing the required dependencies. You might store it on registry.heptapod.host and then use it as the starting point for your job.
The job can make use of services, which will run inside the same virtual machine as the main job.
Here’s a full example making use of a PostgreSQL database, relying on the base image built by our Demo Project for CI image to provide the PostgreSQL client utilities (psql, createdb, etc.)
tests:
image: registry.heptapod.host/heptapod/demos/ci-image:latest
services:
- name: postgres:14 # official Docker image for PostgreSQL on Docker Hub
alias: pgserver # (optional) service host name to use from the job
variables:
# All job environment variables are also set in service containers.
# This one has the effect that postgres will blindly authenticate any
# existing user without any password.
# (the `postgres` image has many more authentication options,
# this one being good enough for our purposes)
# Note: GitLab (Runner) 14.5 will allow setting variables on a
# per-service basis, see https://docs.gitlab.com/ce/ci/services/
POSTGRES_HOST_AUTH_METHOD: trust
script:
- createuser -h pgserver -dSR -U postgres db_owner
- createdb -h pgserver -U db_owner mydb
# Now use the database.
# This query just lists schemas (namepaces) for the sake of example.
- psql -h pgserver -U db_owner -c "SELECT nspname FROM pg_catalog.pg_namespace" mydbDifferences with a Heptapod Runner using the standard Docker executor
Automatic Dependency Proxy
The Dependency Proxy is a standard GitLab Free feature that provides transparent caching of Docker Hub images to minimize bandwidth and avoid rate limiting problems.
With the Clever Cloud Runner, all Docker images from Docker Hub get automatically retrieved from heptapod.host’s Dependency Proxy, By contrast, this is an opt-in feature with the standard Docker executor.
The automatic Dependency Proxy should be mostly transparent to users, except in case of services using a namespaced Docker image and not having an explicit alias. For these, we provide a single service network name whereas the standard executor provides two (replacing forward slashes either by double underscores or dashes). We chose the dash-based RFC compliant one. In short, use octobus-heptapod to reach a service whose Docker image is octobus/heptapod:sometag, or better, set your own explicit alias.
Job cache
Currently, the job cache is discarded at the end of each job.
This is because we don’t have offloading capabilities for the cache yet, and the entire virtual machine gets decommissioned at the end of the job.
We’re working on it and should have a solution soon (see the Persistent cache upcoming feature).
Isolation
Because each job runs in its own transient virtual machine, your jobs are effectively pretty private.
Even if a malicious job were to break the sandboxing provided by Docker itself, it would find nothing to spy on within its Docker host.
Even if your projects are public, this can be an important factor, for instance to protect package signing keys and upload credentials when doing Continuous Delivery.
Docker host flavors
While most of the public CI offering seems to have converged on running jobs on comparatively modest systems (e.g., 2 virtual cores with 7GB of RAM), and many testing frameworks have ways to partition big test suites in several jobs to run in parallel (sharding), this does not fit all needs:
Jobs performing big compilation tasks (OS kernels, desktop applications) may benefit from in-job parallelization and may not be practical to cut in several parallel jobs. At the opposite side of the spectrum, jobs for unit tests or fast linting of small projects may content themselves with a tiny system. In other words, one size does not fit all.
Jobs executed by the Clever Cloud Runner can specify the scale (flavour) of the Docker host it needs, using the CI_CLEVER_CLOUD_FLAVOR variable.
small-job:
variables:
CI_CLEVER_CLOUD_FLAVOR: XS
script:
- ci/display-specs
- ci/lint
bigger-job:
# our base image provides /usr/bin/make
image: registry.heptapod.host/heptapod/demos/ci-image:latest
variables:
CI_CLEVER_CLOUD_FLAVOR: XL
script:
- ci/display-specs
- make all
artifacts:
paths:
- out/binariesDid this documentation help you ?